Technology
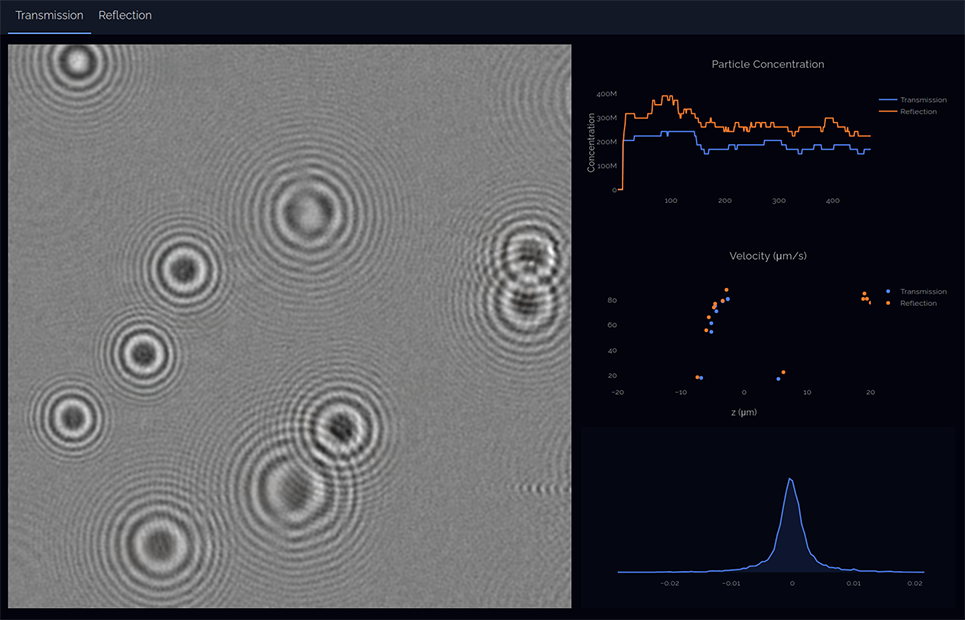
HOLTRA have developed the next generation of nanoparticle analysis technology. Our instrument, DAISY, provides unprecedented detail on any nanoparticle sample with the ease and efficiency of traditional nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA). DAISY is truly a step-change in nanoparticle characterisation, providing all of the information you associate with NTA (size, concentration, polydispersity) but also, for the first time, allowing you to see inside your nanoparticles. DAISY characterises and classifies nanoparticles based on their size, internal mass distribution, refractive index, and geometry. This allows researchers to easily identify, and quantify, sub-populations, such as contaminants or aggregates, within their samples.
The links below provide more information about our technology, or you can click here to see demonstrations of the benefits of our approach in a range of real world applications.
GENERAL OVERVIEW
A brief description of our instrument (DAISY) and the new analytical possibilities it brings to nanoparticle analysis
TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
A more detailed description of the unique technologies underlying DAISY-NTA
PUBLICATIONS
A selection of academic publications outlining the innovations underlying our approach
Features & benefits
- Hydrodynamic diameter
- Optical diameter
- Refractive index
- Morphology/shape
- Particle density
- Concentration
- Size range 50nm – 5 µm
- Single-use microfludic chips